Nearly half of Canadians report that rising prices are greatly impacting their ability to meet day-to-day expenses
Released: 2024-08-15
In spring 2024, nearly half (45%) of Canadians reported that rising prices were greatly affecting their ability to meet day-to-day expenses, 12 percentage points higher than what it was two years earlier (33%).
These results come from the most recent cycle of the Canadian Social Survey, collected from April 19 to June 3, 2024, which focused on indicators from the Quality of Life Framework for Canada and the impact of rising prices. The Quality of Life Framework for Canada is a set of 84 indicators used to measure the overall well-being of Canadians, aiming to inform future policy priorities and improve evidence-based decision making.
This release relates to how rising prices are affecting the ability of Canadians to meet their day-to-day expenses, their concerns with housing affordability, the likelihood that they will obtain food or meals from community organizations, their financial stress, and the relationship between financial stress and quality of life.
Compared with two years earlier, more Canadians are concerned about housing affordability in spring 2024
Concerns about housing affordability increased over the past two years. In spring 2024, nearly 4 in 10 Canadians (38%) reported being very concerned with their ability to afford housing or rent because of rising housing prices, compared with 3 in 10 (30%) in the spring of 2022.
Since 2021, price inflation of food has placed financial strain on Canadians. In spring 2024, more than one in five Canadians (23%) reported their households as being very (8%) or somewhat (15%) likely to obtain food or meals from community organizations over the next six months, similar to the proportion recorded two years earlier (20%).
This extended period of financial strain can also negatively impact mental health. When asked about financial-related stress in spring 2024, more than one-third (35%) of Canadians described most days as quite a bit or extremely stressful due to financial issues. This was similar to the proportion that reported having financial stress two years earlier (33%).
Rising prices have a disproportionate impact on lower-income people in Canada
Rising prices do not affect all Canadians to the same extent. Individuals from lower income groups are struggling more financially due to rising prices than those in higher income groups, consistent with past research. In spring 2024, nearly 6 in 10 of people in the lowest income quintile (59%) and about half of those in the second (52%) and third (48%) income quintiles reported that rising prices greatly affected their ability to meet day-to-day expenses. By comparison, just over one-quarter (27%) of those in the highest income quintile reported experiencing these impacts.
Similarly, people in the lowest income quintile reported having the greatest concern over housing affordability in spring 2024, with nearly half (48%) reporting being very concerned. However, whether somebody rents or owns their home is an important factor for concern about housing affordability. Among those in all but the highest income quintile, about three in five renters (ranging from 58% to 61%) reported being very concerned over housing affordability, compared with about one-third (ranging from 31% to 38%) of homeowners. Renters and owners in the highest income quintile were less likely than those in lower income quintiles to report having this concern.
Recent reports show that people who live in rental housing face greater financial difficulty and report having poorer life satisfaction than those living in a home owned by someone in their household. However, other research suggests that the gap in life satisfaction between renters and owners may be tied to other factors, such as differences in health status, marital status, age and likelihood to experience financial difficulty.
When asked in spring 2024 whether they may need to obtain food or meals from community organizations in the next six months, just over 4 in 10 Canadians in the lowest income quintile (42%) reported their household as being somewhat or very likely to do so. However, many Canadians in higher income quintiles also expected their household to make use of community organizations for food or meals, though the proportions were smaller, at 14% among people in the fourth income quintile and 9% of those in the highest income quintile.
These greater financial pressures for lower-income Canadians have measurable consequences on health and well-being. In spring 2024, nearly half (45%) of people in the lowest income quintile reported most days as being quite a bit or very stressful due to financial concerns, compared with one-quarter (25%) of those in the highest income quintile.
Overall, younger adults are experiencing greater financial difficulty and are more concerned about rising prices
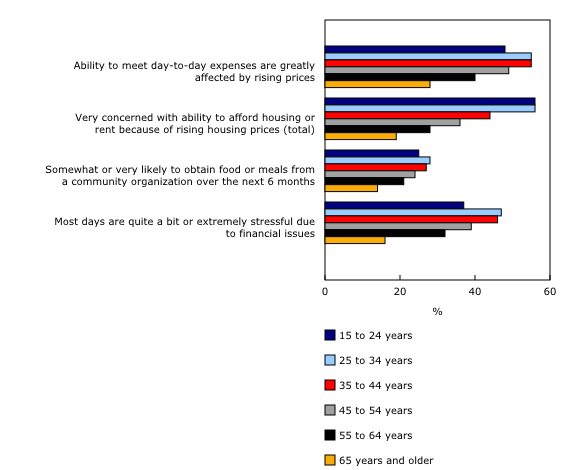
Recent reports found that younger adults are struggling more financially than older Canadians. According to the most recent data, over half (55%) of people aged 25 to 44 years reported that rising prices were greatly affecting their ability to meet day-to-day expenses in spring 2024. By comparison, far fewer seniors (28%) reported having this difficulty. Young adults aged 25 to 44 years were also more likely to report having high financial stress (ranging from 46% to 47%) and expectations to obtain food from a food bank or community organization (ranging from 27% to 28%), particularly compared with seniors.
Housing affordability continues to be a concern among Canadians, particularly among younger adults. In spring 2024, over half (56%) of those aged 15 to 34 years reported being very concerned about housing affordability due to rising housing prices. Concern with housing affordability decreased with age, with one in five Canadians aged 65 years and older (19%) being concerned with housing affordability due to rising prices.
Households with children are experiencing greater financial difficulty due to rising prices than other household types
Related to the finding that young adults are experiencing greater financial difficulty, households with children were more likely to report having financial difficulties in spring 2024 compared with multiple-person households without children and households in which the occupant lived alone.
In spring 2024, over half (55%) of households with children reported that rising prices were greatly affecting their ability to meet day-to-day expenses, which was higher than among multiple person households without children (42%) and lone-occupant households (37%).
Similarly, households with children were also more likely to describe most days as stressful due to financial issues and report being concerned with housing affordability than other household types in spring 2024. Further, just over one-quarter (28%) of households with children expected their household to obtain food or meals from a community organization in the next six months compared with about one in five among other household types. These results align, in part, with prior research, which showed that lone-parent families and other family types were more likely to experience financial distress (e.g., use payday loans) than couples with no children.
Individuals with a disability face greater difficulty making ends meet due to rising prices
Results from the current analysis found that individuals who identified as a person with a disability were consistently more likely to report having financial concerns regarding rising prices compared with those without a disability across all outcomes examined. In spring 2024, over half (57%) of persons with a disability reported that rising prices were greatly affecting their ability to meet day-to-day expenses compared with about 4 in 10 of those without a disability (43%).
In spring 2024, among people who identified as a person with a disability, over 4 in 10 reported being very concerned with housing affordability due to rising prices (43%) and described most days as quite a bit or very stressful due to financial concerns (45%). These proportions were higher than those reported by persons without a disability (38% reported being very concerned with housing affordability due to rising prices and 33% described most days as quite a bit or very stressful due to financial concerns). Regarding rising food costs, just over one-third (34%) of persons with a disability expected that their household would obtain food or meals from a community organization in the next six months compared with about one in five among persons without a disability (21%). Other sources of information have found that the employment rate for persons with a disability was about 20% lower than that for persons without a disability in 2023, and persons with a disability were more likely to live in poverty in 2020. Rising prices may therefore have a disproportionate impact on this population group.
Financial difficulty is associated with lower quality of life
Financial difficulty is known to influence overall well-being. Among those who described most days as quite a bit or very stressful due to financial issues in spring 2024, about one in five (17%) reported having high life satisfaction compared with nearly three-quarters (70%) of those who reported most days as being not at all or not very stressful.
There was a clear difference in hopefulness across groups experiencing different levels of daily stress due to financial issues. In spring 2024, nearly three-quarters (73%) of people who did not report having daily financial stress had a hopeful view of the future compared with just over one-third (35%) of those who found most days quite a bit or extremely stressful due to financial concerns. Previous research found that people experiencing greater economic and social challenges had a less hopeful view of the future than those who did not experience financial hardship.
Overall, findings from the current analysis show that certain groups are experiencing greater financial strain due to rising prices, including those with lower incomes, younger adults, households with children, and persons with a disability. Furthermore, people experiencing greater financial stress are more likely to report having poorer quality of life.
Further insights related to the Quality of Life Framework for Canada can be found on the Quality of Life Hub.
Did you know we have a mobile app?
Download our mobile app and get timely access to data at your fingertips! The StatsCAN app is available for free on the App Store and on Google Play.
Note to readers
This release uses data from the Canadian Social Survey (CSS) (collected from April 19 to June 3, 2024). The target population for the CSS is all non-institutionalized persons 15 years of age or older, living off-reserve in the 10 provinces of Canada. The CSS aims to provide timely information to better understand social issues by conducting surveys on different topics every three months.
Data from the 2022 Portrait of Canadian Society Survey (Impact of rising prices) was also used to compare with previous reported indicators.
Adjusted income quintiles were calculated using self-reported before-tax household income and household size. Estimates for income groups are to be used with caution. Self-reported income data may come with certain inaccuracies and its distribution may be different than the distribution reflected in tax data.
Throughout the text, those who responded "yes, a lot," to the question, "Are rising prices affecting your ability to meet day-to-day expenses?" were considered to have been greatly affected or impacted by rising prices regarding their ability to meet daily expenses.
To identify persons with and without a disability, respondents were asked if they identified as a person with a disability. This differs from the method used by Statistics Canada in the Canadian Survey on Disability, which includes disability screening questions to identify persons with a disability and calculate the official rates of disability in Canada. The Labour Force Survey also uses disability screening questions to identify persons with a disability.
Definitions
High life satisfaction: survey respondents were asked, "Using a scale of 0 to 10, where 0 means 'Very dissatisfied' and 10 means 'Very satisfied,' how do you feel about your life as a whole right now?" In this release, high life satisfaction corresponds to a score of 8, 9 or 10.
Hopeful view of the future: survey respondents were asked, "Thinking about your life in general, how often would you say you have a hopeful view of the future?" Responses of always or often were used in this release to indicate having a hopeful view of future.
Contact information
For more information, or to enquire about the concepts, methods or data quality of this release, contact us (toll-free 1-800-263-1136; 514-283-8300; infostats@statcan.gc.ca) or Media Relations (statcan.mediahotline-ligneinfomedias.statcan@statcan.gc.ca).
- Date modified: