Federal government spending on science and technology, 2019/2020 (intentions)
Archived Content
Information identified as archived is provided for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It is not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards and has not been altered or updated since it was archived. Please "contact us" to request a format other than those available.
Released: 2019-04-01
$11.7 billion
2019/2020
-2.6% 
(annual change)
Federal government science and technology spending intentions are down
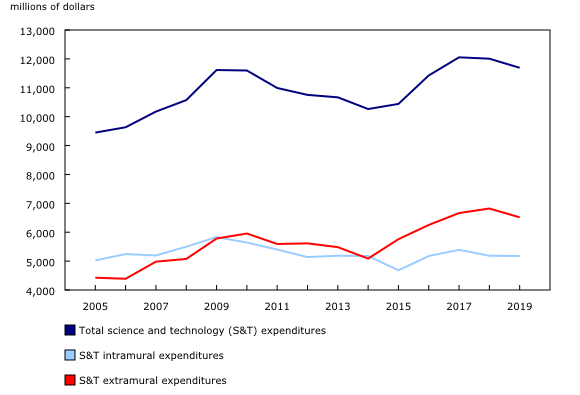
As of December 2018, federal government spending on science and technology (S&T) is expected to decrease by 2.6% to $11.7 billion in 2019/2020. This would be the second consecutive annual decline in S&T spending following three consecutive increases.
S&T includes two components, research and development (R&D) and related scientific activities (RSA). The expected 2.6% decline in S&T spending by the federal government in 2019/2020 is mainly due to an anticipated 6.1% decrease in RSA spending to $4.1 billion. This decline would represent 85% of the expected decrease in total S&T expenditures in 2019/2020. Spending on R&D (both in-house and external) is expected to decline 0.6% to $7.6 billion.
Federal in-house spending on research and development is expected to increase, while spending on related scientific activities is expected to decline
R&D performed by the federal government, also called in-house or intramural spending, is expected to rise 4.7% from a year earlier to $2.2 billion in 2019/2020. Since 2015/2016, the three federal government organizations spending the most on in-house R&D are the National Research Council of Canada, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada and the Department of National Defence. In 2019/2020, these three organizations are expected to account for 60% of total intramural R&D spending by federal departments and agencies.
In-house RSA spending is expected to decline 3.4% to $3.0 billion in 2019/2020. The three departments and agencies with the largest in-house RSA spending are Statistics Canada, Environment and Climate Change Canada and Health Canada, which, combined, are anticipated to account for 44% of all RSA expenditures in 2019/2020.
As a result of anticipated offsetting movements in R&D and RSA spending, total expenditures on federal government in-house S&T are expected to be relatively stable (-0.2%) at $5.2 billion in 2019/2020.
Federal payments to external science and technology performers are expected to decline
Federal government payments to external (or extramural) performers of S&T are expected to decline 4.5% to $6.5 billion in 2019/2020, following increases of 2.3% in 2018/2019 and 6.6% in 2017/2018. Extramural S&T payments are expected to decline for both R&D activities (-2.6% to $5.4 billion) and RSA (-12.6% to $1.1 billion).
External performers that receive funding from the federal government to carry out S&T activities include the following sectors: higher education, provincial and municipal government, business enterprise, private non-profit and foreign. Extramural spending is anticipated to decrease across all performer categories in 2019/2020. Payments to provincial and municipal governments (-52.1%) are expected to be the single largest contributor to the decrease in extramural spending, falling from $259 million to $124 million. The primary reasons for this decline are the expiration of R&D grants and contributions to the provinces for education as well as the completion of a one-time RSA grant to review senior care.
Historically, the higher education sector has received the highest amounts of extramural payments, followed by the business enterprise sector. In 2019/2020, federal payments to the higher education sector are expected to decline 1.2% to $3.6 billion, and the business enterprise sector payments are expected to decrease 4.9% to $1.7 billion. These two sectors are projected to account for 82% of total extramural S&T spending, which would be their largest combined share since 2005.
Little change anticipated in number of federal personnel engaged in science and technology activities
The number of full-time equivalent (FTE) federal government S&T personnel is anticipated to remain largely unchanged in 2019/2020, increasing by 41 FTEs to 36,100. The scientific and professional category is expected to account for over half (56%) of the total federal government S&T full-time equivalents in 2019/2020, while technicians and other personnel categories would make up the remainder.
Note to readers
The Federal Science Expenditures and Personnel survey, Activities in the Social Sciences and Natural Sciences, is an annual survey of all federal government departments and agencies that perform or fund science and technology activities. Actual data for 2017/2018, preliminary data for 2018/2019 and intentions for 2019/2020 were collected from August 15 to November 30, 2018 based on the federal government's fiscal year running from April 1 to March 31.
Science and technology activities comprise two types of scientific activities: research and development, and related scientific activities. They can be defined as all systematic activities which are directly related with the generation, advancement, dissemination and application of scientific and technical knowledge in all fields of science and technology.
Research and development comprises creative and systematic work undertaken in order to increase the stock of knowledge— including knowledge of humankind, culture and society—and to devise new applications of available knowledge.
Related scientific activities are all systematic activities which are directly related with the generation, advancement, dissemination and application of scientific and technological knowledge.
Natural sciences and engineering consist of all disciplines concerned with understanding, exploring, developing or utilizing the natural world. Included are the engineering and technology, mathematical, computer and information sciences, physical sciences, medical and health science, and agricultural sciences, veterinary sciences and forestry.
Social sciences, humanities and the arts consists of disciplines involving the study of human actions and conditions and the social, economic and institutional mechanisms affecting humans. Included are such disciplines as arts, economics and business, education, history and archeology, law, language and linguistics, media and communications, philosophy, ethics and religion, psychology and cognitive sciences, social and economic geography, and sociology.
Full-time equivalent is the personnel expressed as a ratio of working hours actually spent on scientific activities during a specific reference period divided by the total number of hours conventionally worked in the same period by an individual or a group. For example, an employee who is engaged in scientific activities for half a year has a full-time equivalence of 0.5
Scientific and professional personnel (also called Researchers) are professionals engaged in the conception or creation of new knowledge. They conduct research and improve or develop concepts, models and methods. Managers and administrators who plan and manage the scientific and technical aspects of a researcher's work, as well as graduate students, are also included.
Technical personnel perform scientific and technical tasks involving the application of concepts and operational methods in one or more fields of natural sciences and engineering or social sciences, humanities and the arts, normally under the supervision of researchers.
Other personnel (also noted as Support staff) includes skilled and unskilled workers, and administrative, secretarial and clerical staff directly associated with research and development projects.
More information on the concepts and definitions of the survey (4212) is available from this release's Related information tab.
Contact information
For more information, or to enquire about the concepts, methods or data quality of this release, contact us (toll-free 1-800-263-1136; 514-283-8300; STATCAN.infostats-infostats.STATCAN@canada.ca) or Media Relations (613-951-4636; STATCAN.mediahotline-ligneinfomedias.STATCAN@canada.ca).
- Date modified: