Building permits, December 2020
Archived Content
Information identified as archived is provided for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It is not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards and has not been altered or updated since it was archived. Please "contact us" to request a format other than those available.
Released: 2021-01-28
$9.1 billion
December 2020
-4.1% 
(monthly change)
$198.7 million
December 2020
119.9% 
(monthly change)
$42.6 million
December 2020
16.4% 
(monthly change)
$259.7 million
December 2020
62.5% 
(monthly change)
$127.7 million
December 2020
8.1% 
(monthly change)
$1,826.7 million
December 2020
2.2% 
(monthly change)
$3,814.9 million
December 2020
-13.2% 
(monthly change)
$278.7 million
December 2020
5.8% 
(monthly change)
$168.4 million
December 2020
41.8% 
(monthly change)
$895.3 million
December 2020
-12.8% 
(monthly change)
$1,464.1 million
December 2020
-0.1% 
(monthly change)
$5.3 million
December 2020
22.7% 
(monthly change)
$1.3 million
December 2020
-76.7% 
(monthly change)
F
December 2020
F
(monthly change)
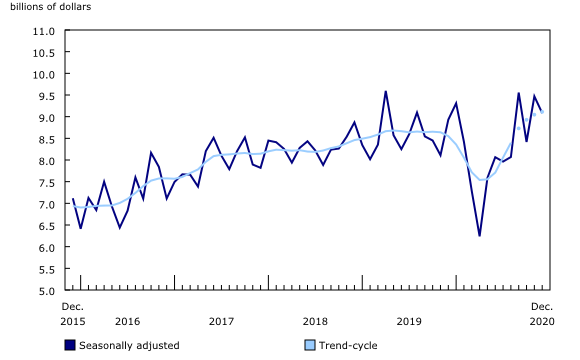
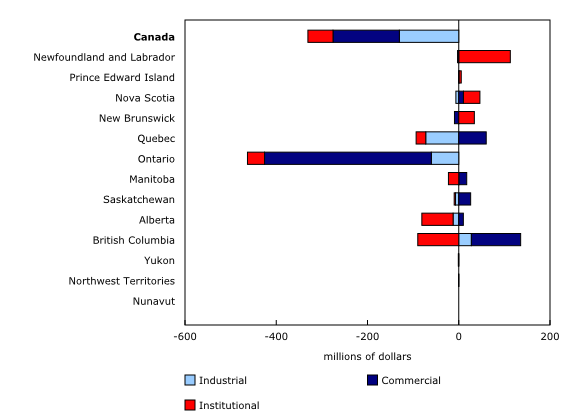
The total value of building permits decreased 4.1% to $9.1 billion in December, following a month during which several high value permits were issued. Declines were reported in every component except single-family dwellings. Gains in seven provinces, led by Newfoundland and Labrador, were largely offset by a significant decrease in Ontario (-13.2%).
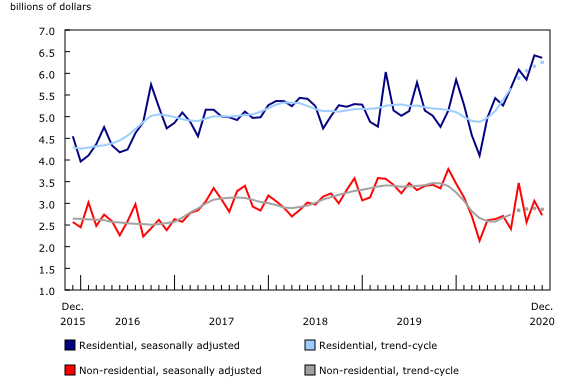
All components decline in the non-residential sector
All three non-residential components—commercial (-9.0%), industrial (-24.4%) and institutional (-6.1%) buildings—reported declines as the overall sector fell 10.8% to $2.7 billion in December.
Four provinces recorded a decrease in the value of non-residential permits. Ontario (-30.5%) posted the largest decline, following a significant increase in the province in the previous month. Excluding Ontario, the value of non-residential permits rose 8.6% in the rest of the country. Newfoundland and Labrador reported its highest value on record ($175 million), which was almost entirely due to a $171 million permit for renovations to a hospital in the city of Corner Brook.
Record high for single-family homes
Single-family homes rose 7.0% to $3.1 billion, surpassing the previous record of $2.9 billion set in October 2016. Six provinces posted gains in this component, led by Ontario (+6.8%) and Quebec (+11.1%). The rise in Ontario was mainly due to the census metropolitan area (CMA) of Toronto (+51.9%), while the gains in Quebec were largely due to municipalities outside of CMAs.
The national value for multi-family dwellings declined 7.2% to $3.3 billion, largely because of a 12.8% drop in Ontario. Four other provinces also reporting a decrease in this component.
Overall, the residential sector edged down 0.9% to $6.4 billion after posting a record setting month in November.
Record quarter due to strength in the residential sector
Quarterly gains observed in the residential sector were enough to offset a decrease in the non-residential sector. As a result, the total value of building permits in the fourth quarter of 2020 reached $27.0 billion, up 5.4% compared with the third quarter, surpassing the previous record high, which was set in the second quarter of 2019.
Single- and multi-family dwellings both posted record highs in the fourth quarter of 2020. This marked the second straight quarter of record-setting numbers for multi-family dwellings, while single-family homes surpassed the previous high set in the fourth quarter of 2016.
Gains in the value of permits issued for institutional buildings (+20.9%) fell short of offsetting reduced activity in the commercial (-10.4%) and industrial (-10.2%) components of the non-residential sector, as the sector as a whole declined 2.8% to $8.3 billion in the fourth quarter.
Annual review of 2020: A year of turbulence
The total value of building permits declined 2.3% in 2020, despite a rebound in the second half of the year. This was the largest annual decrease since the recession in 2009.
The residential and non-residential sectors reversed directions in 2020 as the residential sector posted a record high $66.7 billion, up 7.3%, despite the low values reported in the early spring. In the residential sector, gains in Ontario and Quebec were more than enough to offset the declines in British Columbia. New construction led most of the growth (+9.1%), while permitted renovations dropped 5.0%, largely as a result of fewer projects for multi-family dwellings.
Over two-fifths (41.6%) of Canadians reported working half or more of their usual work hours from home during the early stages of the pandemic, according to the Labour Force Survey. This share had declined to 28.6% by December 2020, but was still more than double pre-pandemic levels. The need for more personal space, including room for home offices, accompanied by historically low mortgage rates and higher disposable income, has strongly influenced the housing markets. The value of permits for single-family homes rose 8.0% in 2020 to its fifth highest annual value on record ($28.7 billion).
Overall, the value of multi-family dwelling permits continued the upward trend observed over the past 10 years, increasing 6.8% to a record high of $38.0 billion. Typically associated with larger yards and interior space compared with other multi-family ownership properties such as condos (-4.4%), semi-detached homes (+24.2%) were one of the two categories of multi-family dwellings to record a notable gain in 2020.
As more Canadians work from home, demand for commercial office space has dwindled. According to the Canadian Survey on Business Conditions, many businesses reported that they would to continue to offer their employees the possibility of working remotely once the pandemic is over. In the year, the value of permits issued for office buildings fell 9.8%.
Overall, the non-residential sector posted the largest decline since 2009, down 17.0% to $33.8 billion—the lowest value in four years. All components were down in 2020, with the commercial component setting a record drop of 21.2% and reaching its lowest level since 2017. Going against the grain, Ontario commercial permits increased 5.1%, as a result of large developments such as Project Python in the city of Ottawa, the Breithaupt Block office building in the city of Kitchener and the Cadillac Fairview office building in the city of Toronto.
To explore the impact of COVID-19 on the socioeconomic landscape, please visit the Canadian Economic Dashboard and COVID-19.
For more information on housing, please visit the Housing statistics portal.
Statistics Canada has a Housing Market Indicators dashboard. This web application provides access to key housing market indicators for Canada, by province and by census metropolitan area. These indicators are updated automatically with new information from monthly releases, giving users access to the latest data.
Note to readers
Unless otherwise stated, this release presents seasonally adjusted data, which facilitate month-to-month comparisons by removing the effects of seasonal variations. For information on seasonal adjustment, see Seasonally adjusted data – Frequently asked questions.
All annual data is presented as unadjusted data.
The Building Permits Survey covers over 2,400 municipalities, representing 95% of the Canadian population. The communities representing the other 5% of the population are very small, and their levels of building activity have little impact on the total for the entire population.
Building permit data are used as a leading indicator of activity in the construction industry.
The value of planned construction activities presented in this release excludes engineering projects (such as waterworks, sewers or culverts) and land.
For the purposes of this release, the census metropolitan area of Ottawa–Gatineau (Ontario and Quebec) is divided into two areas: the Ottawa part and the Gatineau part.
Unless otherwise specified, the highlights refer to seasonally adjusted current dollars and are ranked in terms of dollar change rather than percentage change.
Building components
Single-family dwellings: Residential buildings containing only one dwelling unit (for example, single-detached house, bungalow, linked home [linked at the foundation]).
Multi-family dwellings: Residential buildings containing multiple dwelling units (for example, apartment, apartment condominium, row house, semi-detached house).
Industrial buildings: Buildings used in the processing or production of goods, or related to transportation and communication.
Commercial buildings: Buildings used in the trade or distribution of goods and services.
Institutional and government buildings: Buildings used to house public and semi-public services, such as those related to health and welfare, education, or public administration, as well as buildings used for religious services.
Revision
Unadjusted data for the current reference month are subject to revision based on late responses. Data for the previous two months have been revised. Seasonally adjusted data for the previous three months have also been revised.
Trend-cycle estimates have been added to the charts as a complement to the seasonally adjusted series. Both seasonally adjusted data and trend-cycle estimates are subject to revision as additional observations become available. These revisions could be large and could even lead to a reversal of movement, especially at the end of the series. The higher variability associated with trend-cycle estimates is indicated with a dotted line on the chart.
For information on trend-cycle data, see the StatCan Blog and Trend-cycle estimates – Frequently asked questions.
Next release
Data on building permits for January will be released on March 3, 2021.
Contact information
For more information, or to enquire about the concepts, methods or data quality of this release, contact us (toll-free 1-800-263-1136; 514-283-8300; STATCAN.infostats-infostats.STATCAN@canada.ca) or Media Relations (613-951-4636; STATCAN.mediahotline-ligneinfomedias.STATCAN@canada.ca).
- Date modified: