Education Indicators in Canada: An International Perspective, 2018
Chapter B
Financial resources invested in education
Archived Content
Information identified as archived is provided for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It is not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards and has not been altered or updated since it was archived. Please "contact us" to request a format other than those available.
B1 Expenditure per student
Context
This indicator provides information on the investment, from all sources, in each student in public and private institutions at several levels of education. Expenditure by educational institutions per student is largely influenced by teachers’ salaries (see Indicators B3 and C3), pension systems, teaching and instructional hours (see Indicators C1, C2), the cost of teaching materials and facilities, the program provided (e.g., general or vocational), and the number of students enrolled in the education system. Policies to attract new teachers or to reduce average class size or change staffing patterns have also contributed to changes in expenditure by educational institutions per student over time. Ancillary and R&D services can also influence the level of expenditure by educational institutions per student.
Effective schools require the right combination of trained and talented personnel, appropriate curriculum, adequate facilities and motivated students who are ready to learn. The demand for high quality education, which can translate into higher costs per student, must be balanced against other demands on public expenditure and the overall burden of taxation. Although it is difficult to assess the optimal volume of resources needed to prepare each student for life and work in modern societies, international comparisons of spending by educational institutions per student can provide useful reference points.
Policy-makers must also balance the importance of improving the quality of educational services with the desirability of expanding access to educational opportunities, notably at the tertiary level. In addition, decisions regarding the allocation of funds among the various levels of education are key. For example, certain provinces and territories emphasize broad access to higher education and some invest in near universal education for children as young as 3 or 4 years of age.
The indicator shows direct public and private expenditure by educational institutionsNote 1 in relation to the number of full-time equivalent students enrolled. Note that variations in expenditure by educational institutions per student may reflect not only variations in the resources provided to students (e.g., variations in the ratio of students to teaching staff) but also variations in relative salary and price levels.Note 2
Observations
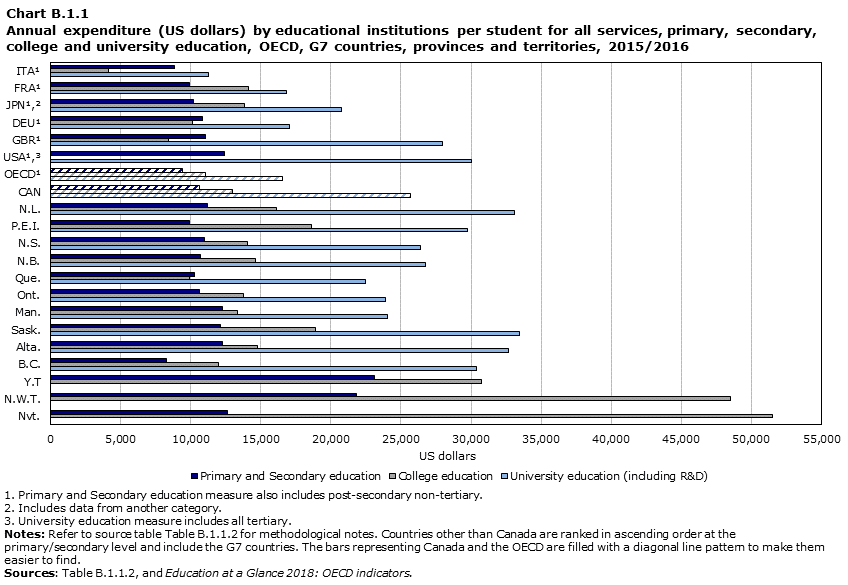
Data table for Chart B.1.1
| Primary and Secondary education | College education | University education (including R&D) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| US dollars | |||
| Nvt. | 12,613 | 51,527 | Note ...: not applicable |
| N.W.T. | 21,819 | 48,506 | Note ...: not applicable |
| Y.T | 23,104 | 30,753 | Note ...: not applicable |
| B.C. | 8,297 | 11,964 | 30,414 |
| Alta. | 12,286 | 14,782 | 32,663 |
| Sask. | 12,109 | 18,931 | 33,469 |
| Man. | 12,243 | 13,310 | 24,033 |
| Ont. | 10,618 | 13,733 | 23,928 |
| Que. | 10,267 | 9,940 | 22,441 |
| N.B. | 10,706 | 14,632 | 26,757 |
| N.S. | 11,003 | 14,085 | 26,419 |
| P.E.I. | 9,942 | 18,602 | 29,780 |
| N.L. | 11,225 | 16,088 | 33,120 |
| CAN | 10,639 | 12,995 | 25,659 |
| OECDData table Note 1 | 9,401 | 11,022 | 16,518 |
| USAData table Note 1 Data table Note 3 | 12,424 | Note ...: not applicable | 30,003 |
| GBRData table Note 1 | 11,028 | 8,421 | 27,931 |
| DEUData table Note 1 | 10,863 | 10,149 | 17,036 |
| JPNData table Note 1 Data table Note 2 | 10,167 | 13,806 | 20,758 |
| FRAData table Note 1 | 9,897 | 14,093 | 16,805 |
| ITAData table Note 1 | 8,831 | 4,120 | 11,285 |
... not applicable
Sources:Table B.1.1.2 and Education at a Glance 2018: OECD indicators. |
|||
- Expenditure per student at the primary/secondary level was similar for Canada, the provinces, other G7 countries and the OECD average. In the territories, the structural costs associated with delivering education at the primary and secondary, and college level tend to be higher than those in the provinces .
- For primary/secondary levels, educational core services represented the bulk of expenditure per student in Canada, and across provinces and territories, ranging from 93% for the Newfoundland and Labrador, to 99% in Yukon. The corresponding OECD average was similar at 94% of total expenditures on core education.
- For the college level (short cycle tertiary), expenditure per student in Canada (US$12,995) was higher than the OECD average (US$11,022). For the available G7 countries, there was a range with Itally being the lowest and Canada being in the middle behind Japan and France. Within Canada, between provinces there was also variation, with Saskatchewan and Prince Edward Island being the highest and Quebec being the lowest.
- For the university level, at US$25,659, Canada’s figure was 55% higher than the OECD average of US$16,518, but was third highest in the G7 behind the United Kingdom and United States.
- Similar to the OECD averages, in Canada and every province except Quebec, expenditure per student was lowest at the primary/secondary level, higher at the college level and highest at the university level. In Quebec, college expenditure per student was slightly lower than that of expenditure per student at the primary/secondary level.
Definitions, sources and methodology
Data refer to the 2015/2016 financial year and the 2015/2016 school year. Unlike previous publications, the financial and enrolment data here are not processed to reflect a single calendar year. These data are collected for the elementary and secondary levels as well as for the college and university sectors. The OECD figures are from the UOE data collection on education statistics, administered by the OECD in 2017.Note 3
Expenditure per student by educational institutions at a given level of education is calculated by dividing the total expenditure by educational institutions at that level by the corresponding full-time equivalent (FTE) enrolment. Only educational institutions and programs for which both enrolment and expenditure data are available are taken into account. In accordance with the OECD definition provided in the data collection manual, debt servicing expenditure is excluded.
Financial data for elementary and secondary school levels are based on three Statistics Canada surveys: the Survey of Uniform Financial System – School Boards (this is the largest source of expenditure reporting); the Elementary-Secondary Education Survey (ESES) and the Survey of Federal Government Expenditures in Support of Education (FEDEX). The survey data are consolidated with federal and provincial expenditures on education, and other sources of revenue, to give a more complete picture of government expenditures.
Enrolment data for elementary and secondary school levels are the sum of enrolment in public and private schools (ESES), and enrolment in First Nations band-operated schools (Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada).
In Quebec, vocational training and general education for adults are included at the secondary level. Given that a significant number of these enrolments are part time, the headcounts were adjusted to FTE enrolments using a factor of 0.6 for vocational training, and 0.2 for adult education. Students enroled in regular programs for youth who were over 21 years of age were treated as part-time and a factor of 0.2 was applied. Due to these changes, this year’s estimate of expenditure per student is not comparable with estimates from previous years (publication years 2017 or earlier).
Financial data for the college level came from the Financial Information of Community Colleges and Vocational Schools Survey (FINCOL). For the university sector, the financial data were drawn from the Financial Information of Universities and Colleges Survey (FIUC), done in conjunction with the Canadian Association of University Business Officers (CAUBO), and the Survey of Federal Government Expenditures in Support of Education (FEXEX). These survey data are then consolidated with federal and provincial expenditures on education, and other sources of revenue, to give a more complete picture of government expenditures at the two levels.
Subsequently, educational institutions that have both enrolment as well as expenditure data are kept in the analysis. For college, if an institution has expenditure data but no enrolment, the FINCOL value for that college is subtracted from the total expenditure. For university, where there is more complete coverage, if an institution has expenditure data but no enrolment data, the enrolment data was estimated based on public information.
The enrolment figures for both the college and university levels come from the Postsecondary Student Information System (PSIS). In the case of colleges, a new methodology was used in order to calculate full-time equivalent enrolments. This method used course-level data in order to estimate a ratio for caluclating the number of full-time equivalent enrolments. Apprentices were treated as full-time students due to their high resource use while they are in school sessions.
For university, student-program enrolments on a given day from the fall term were used to approximate a full-time enrolment count. Part-time students identified in this count were divided by 3.5 and added to the number of full-time students.
In addition, for both the university and college sectors, financial data are collected at an institutional level only, and thus cannot be divided by type of program. As a result, expenditures also include any expenditure for programs that are not at the diploma, Bachelor’s, Master’s, or Doctoral levels such as career, technical or professional training programs. In order to be consistent, enrolment for these additional programs have also been retained in the analysis.
For comparison with the OECD, expenditure in Canadian currency was converted into equivalent US dollars by dividing the national currency figure by the purchasing power parity (PPP) index for the gross domestic product (GDP). The value of 1.25 (for 2015/2016) was used. The PPP index was used because the market exchange rate is affected by many factors (interest rates, trade policies, economic growth forecasts, etc.) that have little to do with current relative domestic purchasing power in different OECD countries. Expenditure data are not adjusted for the differences in the cost of living across the provinces and territories.
Educational core services are the expenditure portion that covers the real mission of educational institutions, which is to provide education. There are also expenditures on ancillary services, which have two main components: student welfare services (transportation, lodging and meals) and services for the general public (museums, radio and cultural programs). In the university and college sector, ancillary services typically include bookstores, food services (dining hall, cafeterias and vending machines), residences and housing, parking, university press publishing, laundry services, property rentals, university facility rentals, theaters, and conference centers.
Education expenditure at the university level also includes expenditure on research and development, such as subsidies received by the institution for research projects and an estimate of the proportion of other current expenditures allocated to research and development.
The OECD average is calculated as the average of all OECD countries for which data are available.
Note: The corresponding OECD indicator is C1, How much is spent per student on educational institutions?.
B2 Expenditure on education as a percentage of GDP
Context
This indicator provides a measure of the proportion of national wealth that is invested in educational institutions by linking public and private expenditures with gross domestic product (GDP).
Expenditure on education is an investment that can help foster economic growth and enhance productivity. Education contributes to personal and social development and reduces social inequality. The allocation of financial resources to educational institutions is a collective choice, made by government, business, and individual students and their families. It is partially influenced by the size of the school-age population and enrolment in education, as well as relative wealth.
Observations
GDP allocated to educational institutions

Data table for Chart B.2.1
| All primary, secondary | All postsecondary | |
|---|---|---|
| percent | ||
| DEU | 2.8 | 1.4 |
| FRA | 3.7 | 1.5 |
| GBR | 4.4 | 1.9 |
| ITA | 3.0 | 1.0 |
| JPN | 2.7 | 1.4 |
| USA | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| OECD | 3.5 | 1.6 |
| CAN | 3.4 | 2.4 |
| N.L. | 3.0 | 2.4 |
| P.E.I. | 4.0 | 3.4 |
| N.S. | 4.1 | 3.7 |
| N.B. | 4.0 | 2.5 |
| Que. | 3.7 | 2.6 |
| Ont. | 3.7 | 2.6 |
| Man. | 4.6 | 2.6 |
| Sask. | 3.9 | 2.1 |
| Alta. | 2.8 | 1.9 |
| B.C. | 2.7 | 2.6 |
| Y.T. | 5.5 | 2.1 |
| N.W.T. | 4.5 | 1.4 |
| Nvt. | 6.2 | 2.6 |
|
Notes: For the OECD, the total expenditure on all levels of education combined was 5.1% of GDP, which also included "undistributed programmes" (Table B.2.1). All postsecondary includes post-secondary non-tertiary for Canada. The OECD average excludes postsecondary non-tertiary. The bars representing Canada and the OECD are filled with a diagonal line pattern to make them easier to find. Sources: Table B.2.1 and Education at a Glance 2018: OECD Indicators. |
||
- With 6% of its GDP allocated to educational institutions in 2015/2016 (3% for primary and secondary education plus 2% for all postsecondary education), Canada devoted more than the 5% average estimated by the OECD average (4% and 2% respectively).Note 4
- The financial commitment to educational institutions varied from one province or territory to another, ranging from 5% of GDP in Newfoundland and Labrador, Alberta and British ColumbiaNote 5 to 9% in Nunavut,Note 6 in 2015/2016.
- Within the G7 countries, the range was from 4% to 6%.
Share of wealth invested in primary and secondary versus tertiary education
- In all G7 countries, Canada included, and at the OECD average, the share of national wealth invested in education was larger for primary and secondary education than that for tertiary education in 2015/2016.
Definitions, sources and methodology
This indicator shows expenditure (public and private) with regard to educational institutions as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP), by level of education and for all levels of education combined.
"Expenditure on educational institutions" includes spending on both instructional and non-instructional educational institutions. Instructional educational institutions are entities that provide instructional programmes (e.g., teaching) to individuals directly in an organized group setting or through distance education.Note 7 Non-instructional educational institutions are entities that provide advisory, administrative or professional services to other educational institutions but do not enrol students themselves.
Canada classifies expenditure by education level in a way that differs slightly from that of most other countries; that is, expenditure on pre-elementary education is grouped with expenditure at the elementary and secondary levels, while expenditure on postsecondary non-tertiary education (essentially technical and vocational training) is grouped with tertiary-type B expenditure. This should not affect international comparability, however, since expenditure at the elementary and secondary levels is dominant.
The financial data for Canada were drawn from five Statistics Canada surveysNote 8 and exclude expenditure related to debt service. GDP data were provided by the System of National Accounts Branch. All data for Canada, the provinces and territories refer to the 2015/2016 financial year. The OECD averages (for the 2015 financial year) are based on data from all countries collected by the OECD through the UOE data collection on educational systems, conducted jointly by three international organizations (UNESCO, the OECD and Eurostat) and administered by the OECD in 2017.
Note: The corresponding OECD indicator is C2, What proportion of national wealth is spent on education?.
B3 Distribution of expenditure on education
Context
This indicator outlines spending on education services and resources, identifying the proportion of budgets allocated to currentNote 9 and capitalNote 10 expenditures. A breakdown of current spending—compensation of teachers, other staff and other expenses—is also presented.
The distribution of expenditures may be influenced by a number of factors, including compensation for teachers, the generosity of pension plans, the size of the non-teaching staff, and the different needs for infrastructure. Budget allocation can affect the quality of services, the condition of equipment, and the ability of the education system to adapt to changes in enrolments. Both budgetary and structural decisions taken at the system level have repercussions extending into the classroom: they influence the nature of instruction and the conditions in which it is provided.
Observations
Current and capital expenditures
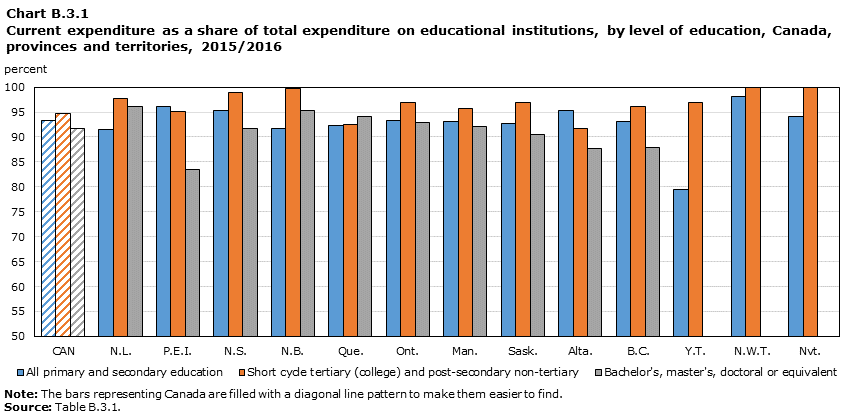
Data table for Chart B.3.1
| All primary and secondary education | Short cycle tertiary (college) and post-secondary non-tertiary | Bachelor's, master's, doctoral or equivalent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| percent of total expenditure | |||
| CAN | 93.3 | 94.7 | 91.8 |
| N.L. | 91.5 | 97.7 | 96.1 |
| P.E.I. | 96.2 | 95.2 | 83.5 |
| N.S. | 95.3 | 99.0 | 91.8 |
| N.B. | 91.7 | 99.8 | 95.2 |
| Que. | 92.2 | 92.5 | 94.2 |
| Ont. | 93.4 | 97.0 | 93.0 |
| Man. | 93.2 | 95.8 | 92.2 |
| Sask. | 92.8 | 96.8 | 90.5 |
| Alta. | 95.4 | 91.6 | 87.8 |
| B.C. | 93.1 | 96.1 | 87.8 |
| Y.T. | 79.4 | 96.9 | Note ...: not applicable |
| N.W.T. | 98.1 | 100.0 | Note ...: not applicable |
| Nvt. | 94.1 | 100.0 | Note ...: not applicable |
|
... not applicable Note: The bars representing Canada are filled with a diagonal line pattern to make them easier to find. Source: Table B.3.1. |
|||
- In 2015/2016, the rate of spending on current expenditure exceeded that on capital expenditure at all levels of education for Canada, provinces, territories and in all OECDNote 11 countries. In Canada, current expenditure accounted for 93% of total expenditure at primary and secondary education levels; 95% for short cycle tertiary (college) and post-secondary non-tertiary level, and 92% for bachelor's, master's, doctoral or equivalent.
- Overall, the highest current spending rate was observed at the level of short cycle tertiary (college) and post-secondary non-tertiary. Within the provinces and territories, this rate varied from 79% for Manitoba to 100% for New Brunswick, Northwest Territories and Nunavut.Note 12
- At the postsecondary level,Note 13 capital expenditure was 7% in Canada, compared with 12% for the OECD average.
Compensation of all staff and compensation of teachers

Data table for Chart B.3.2
| All primary and secondary education | Short cycle tertiary (college) and post-secondary non-tertiary | Bachelor's, master's, doctoral or equivalent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| percent of current expenditure | |||
| CAN | 80.3 | 66.3 | 66.0 |
| N.L. | 81.3 | 69.5 | 68.2 |
| P.E.I. | 83.2 | 63.4 | 71.6 |
| N.S. | 73.3 | 65.8 | 63.7 |
| N.B. | 76.5 | 69.0 | 67.3 |
| Que. | 78.0 | 71.5 | 67.9 |
| Ont. | 83.9 | 63.8 | 64.2 |
| Man. | 76.6 | 68.1 | 63.6 |
| Sask. | 74.5 | 66.2 | 63.3 |
| Alta. | 78.7 | 65.0 | 66.5 |
| B.C. | 79.3 | 66.2 | 69.5 |
| Y.T. | 77.4 | 58.6 | Note ...: not applicable |
| N.W.T. | 68.1 | 60.5 | Note ...: not applicable |
| Nvt. | 87.3 | 66.0 | Note ...: not applicable |
|
... not applicable Note: The bars representing Canada are filled with a diagonal line pattern to make them easier to find. Source: Table B.3.1. |
|||
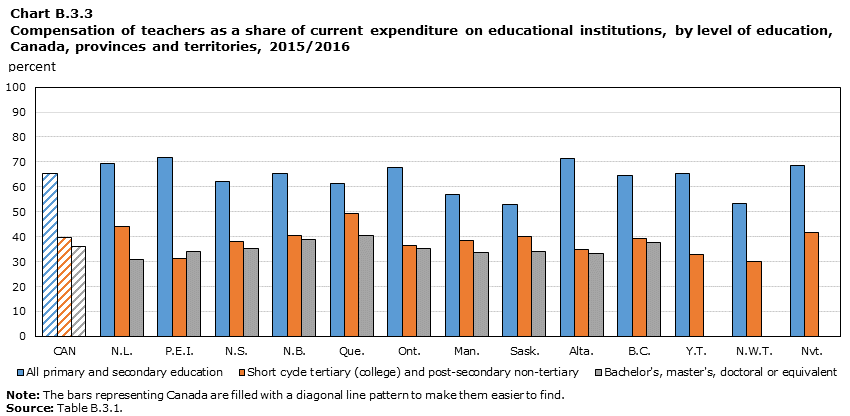
Data table for Chart B.3.3
| All primary and secondary education | Short cycle tertiary (college) and post-secondary non-tertiary | Bachelor's, master's, doctoral or equivalent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| percent of current expenditure | |||
| CAN | 65.3 | 39.8 | 36.2 |
| N.L. | 69.2 | 44.0 | 30.9 |
| P.E.I. | 71.9 | 31.2 | 34.0 |
| N.S. | 62.2 | 38.0 | 35.1 |
| N.B. | 65.4 | 40.4 | 39.0 |
| Que. | 61.2 | 49.4 | 40.6 |
| Ont. | 68.0 | 36.5 | 35.3 |
| Man. | 57.1 | 38.6 | 33.8 |
| Sask. | 52.9 | 40.2 | 34.0 |
| Alta. | 71.3 | 34.8 | 33.1 |
| B.C. | 64.4 | 39.4 | 37.7 |
| Y.T. | 65.5 | 32.9 | Note ...: not applicable |
| N.W.T. | 53.5 | 30.0 | Note ...: not applicable |
| Nvt. | 68.4 | 41.5 | Note ...: not applicable |
|
... not applicable Note: The bars representing Canada are filled with a diagonal line pattern to make them easier to find. Source: Table B.3.1. |
|||
- At all levels of education and in all provinces and territories, the compensation of staff (teaching and non-teaching) accounted for the largest proportion of current expenditure on education. In Canada, it represented on average 80% of current expenditure at the primary and secondary levels, and 66% at both the short cycle tertiary (college) and postsecondary non-tertiary level, and the university level.
- In all provinces and territories, the proportion of spending related to compensation of staff was highest in primary and secondary education, ranging from 68% in the Northwest Territories to 87% in Nunavut.
- For primary and secondary education, compensation of teachers accounted for the largest proportion of compensation of staff. In Canada, compensation of teachers at these levels represented 65% of current spending in 2015/2016, compared with 15% for compensation of other staff. This difference was less pronounced at the short cycle tertiary (college) and postsecondary non-tertiary level and at the university level.
- Other current expenditure was higher at the postsecondary level than at the primary and secondary levels. For 2015/2016, the Canadian average was 34% for short cycle tertiary (college) and postsecondary non-tertiary education, as well as for university education, compared with 20% for primary and secondary education. The OECD average for other expenditure at the postsecondary level was 32%, similar to the Canadian average.
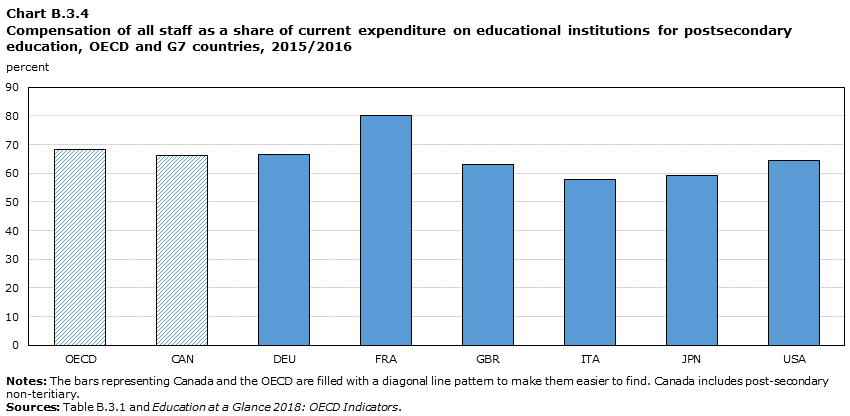
Data table for Chart B.3.4
| Compensation of all staff as a share of current expenditure for postsecondary education | |
|---|---|
| percent | |
| OECD | 68.4 |
| CAN | 66.1 |
| DEU | 66.7 |
| FRA | 80.3 |
| GBR | 63.2 |
| ITA | 57.9 |
| JPN | 59.4 |
| USA | 64.4 |
|
Notes: The bars representing Canada and the OECD are filled with a diagonal line pattern to make them easier to find. Canada includes post-secondary non-teritiary. Sources: Table B.3.1 and Education at a Glance 2018: OECD Indicators. |
|
- For the OECD and the G7 averages, compensation of staff (teaching and non-teaching) made up the largest proportion of current expenditure for postsecondary education. Among G7 countries, this expenditure varied from 58% in Italy to 80% in France, whereas the Canadian and OECD averages were 66% and 68% respectively.
Definitions, sources and methodology
This indicator shows the proportion of budgets allocated to current and capital spending at different education levels. Expenditures are based on accrual and cash (or fund) accounting, depending on the data source(s) used by the provinces/territories. It also shows the proportion of current expenditure allocated to compensation of teachers and of other staff, along with other current expenditure.
The distinction between current expenditure and capital expenditure is taken from the standard definition used in national accounts. Current refers to resources used each year by institutions as they carry out their activities. It includes research and development expenditures, which are not capital expenditures. Capital covers assets that last longer than one year, including spending on new or replacement equipment and construction or renovation of buildings. Neither takes expenditure related to debt service into account.
Expenditure on educational core services includes all expenditure directly related to instruction and education; i.e., all expenditure on teachers, school buildings, teaching materials, books and administration of schools.
The data for Canada reflect the 2015/2016 financial year, and figures were drawn from five Statistics Canada surveys: the Elementary-Secondary Education Survey; the Survey of Uniform Financial System-School Boards; the Financial Information of Universities and Colleges Survey; the Survey of Federal Government Expenditures in Support of Education and Financial Information of Community Colleges and Vocational Schools. Information for OECD member countries, and the OECD averages, refer to data for the 2015 financial year and are based on the data collection on educational systems conducted jointly by three international organizations—UNESCO, the OECD and Eurostat—and administered by the OECD.
Note: The corresponding OECD indicator is C6, On what resources and services is education funding spent?.
- Date modified:
