Employment changes across industries during the downturn and recovery
Archived Content
Information identified as archived is provided for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It is not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards and has not been altered or updated since it was archived. Please "contact us" to request a format other than those available.
The article "Employment changes across industries during the downturn and recovery" was reloaded on April 25th, 2012. A classification error was notified in Table 2, which mainly affected the distribution of ‘pro-cyclical’ industries during the last three downturn and recovery periods (with little variation in the results for the latest downturn). These revisions affect data in Table 2 and the associated text.

by Sharanjit Uppal and Sébastien LaRochelle-Côté
[Release from The Daily] [Full article in PDF]
- Overview of the study
- Introduction
- Employment levels recovered faster in the 2000s
- Employment changes across industries
- More workers employed in industries that did not fully recover in the 1990s
- What happened during the recent post-recovery period?
- Conclusion
- Related material for this article
Overview of the study
During downturns and the subsequent recovery periods, not all industries follow a cyclical pattern of job losses followed by sustained growth. Some industries may lose ground in the downturn and remain stagnant during the recovery, while others register net gains during both the downturn and the recovery. This study examines employment changes across industries over the course of the last three downturns and subsequent recoveries. It also examines the sectors that have been drivers of job growth since the end of the most recent recovery period.
- After the recent downturn, during which employment declined by 431,000 (from October 2008 to July 2009), the labour market took 18 months (until January 2011) to recover all jobs that had been lost.
- In October 2008—when the downturn began—23% of employed individuals were in industries—like health care services—that expanded during both the downturn and the recovery. Another 47% were in industries—like professional, technical and scientific services—that either expanded during the recovery, significantly recovered from their losses, or did not experience large employment fluctuations.
- Conversely, 20% were in industries that declined during both the downturn and the recovery, or did not recover from all their losses during the recovery (like manufacturing). The rest (11%) were in industries that followed a countercyclical pattern—growing during the downturn and downsizing during the recovery.
- In the 1990s, 448,000 jobs were lost during the downturn and the labour market took 25 months to recover. In April 1990, when the downturn began, more workers (31%) were employed in industries that either declined both during the downturn and the recovery or did not fully recover after the downturn.
- Since the end of the recent recovery period (from January 2011 to February 2013), employment increased by 463,000. Nearly three-quarters of employment gains were in accommodation and food services, health care and social assistance, educational services, and construction.
Introduction
In the late 2000s, most of the world’s economies experienced a slowdown. The global economic decline began in December 2007 and took a sharp turn in September 2008. Canada itself was not immune from this slowdown. Output in Canada started to decline in the third quarter of 2008 and reached a low point in the second quarter of 2009.Note 1 Similarly, employment started declining in the third quarter of 2008 and reached a low point in the third quarter of 2009.Note 2
During recovery periods, employment gains do not always move in tandem with output gains. Following the recession of the early 1990s, for example, employment growth resumed a year and a half after output started expanding, giving rise to a period of 'jobless recovery.'
Following the more recent recession, employment and output recovered at almost the same pace—output growth resumed in the second quarter of 2009 and was followed by employment growth the following quarter, suggesting that conditions faced by the labour market were different in the late 2000s.
One hypothesis to explain the longer recovery in the 1990s is that job changes were more transformative or ‘structural’ during that period. Structural changes are labour market changes that imply a shift of resources across industries, requiring many workers to retrain or develop new skills. In contrast, 'cyclical' flows are less transformative in nature, with workers more likely to return to their former jobs or find comparable employment in similar industries.Note 3 Information about the nature and extent of such changes is therefore important, especially for policy makers and central bankers.
One key indicator of labour market transformation during recessions is the degree of employment changes across industries.Note 4 On one hand, if most employment flows that occur within industries are driven by cyclical factors, fewer changes are likely affecting the labour market. On the other hand, if employment declines in some industries have been followed by gains in others, more fundamental changes are probably taking place in the labour market.
Using data from the most recent Labour Force Survey (see Data sources, methods and definitions), this report examines employment patterns across industries during the recent recession, and provides comparisons with the recessions of the early 1980s and early 1990s. It also looks at the drivers of employment growth during the most recent post-recovery period.
Employment levels recovered faster in the 2000s
Before looking at job flows across industries, it is useful to examine the number of months from when employment losses first began to when employment levels reached their low point (i.e., the duration of the employment downturn) and the number of months from the employment low point to when employment levels returned to pre-recessionary levels (i.e., the duration of the recovery).
During the recent downturn, employment levels started falling in October 2008 and hit a low point 9 months later, in July 2009 (Table 1). In total, employment declined by 431,000, or 2.5% of the workforce. It took 18 months to reach pre-recessionary employment levels—meaning that employment had climbed back to its pre-downturn level by January 2011.
Table 1
Duration of downturns and recoveries (in months)
| Duration of downturn | Duration of recovery | Total | Employment losses during the downturn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| months | thousand | percentage | |||
| Beginning of downturn | |||||
| October 2008 | 9 | 18 | 27 | 431.3 | 2.5 |
| April 1990 | 28 | 25 | 53 | 447.6 | 3.4 |
| June 1981 | 17 | 23 | 40 | 611.5 | 5.4 |
| Source: Statistics Canada, Labour Force Survey, 1981 to 1984, 1990 to 1994, 2008 to 2011. CANSIM table 282-0088. | |||||
In contrast, the downturns of the early 1980s and 1990s were more severe and prolonged. Starting in June 1981, the economy shed 5.4% of its workforce over a period of 17 months, and took another 23 months to recover the losses. The downturn of the 1990s was even more prolonged as it took 28 months to reach a low point and another 25 months to regain the 3.4% decline in employment.
The more severe job losses of the 1980s and the protracted recovery period of the 1990s raise the possibility that the Canadian economy faced a higher degree of transformation at the time. While cyclical changes within industries may be less transformative (laid-off workers may be recalled to their old jobs or may find comparable employment with similar firms), employment changes resulting from changes in the industrial structure bring a different set of labour market challenges as more workers may need to develop new skills and competencies.
Employment changes across industries
Changes in the industrial structure can be studied by tracking employment patterns across industries during the downturn and the subsequent recovery.Note 5 Cyclical changes in employment are evident when employment losses in an industry occur during recessionary periods but are reversed during the subsequent recovery. In contrast, structural changes may be evident when employment losses (or gains) occur during both the recessionary and the recovery periods of the business cycle.
Industries can be grouped into four categories based on the percent change in employment during the downturn period (from October 2008 to July 2009) and during the subsequent recovery period (from July 2009 to January 2011):Note 6
- pro-cyclical industries—declining during the downturn and growing during the recovery
- countercyclical industries—growing during the downturn and declining during the recovery
- industries declining during both the downturn and the recovery
- industries growing during both the downturn and the recovery.
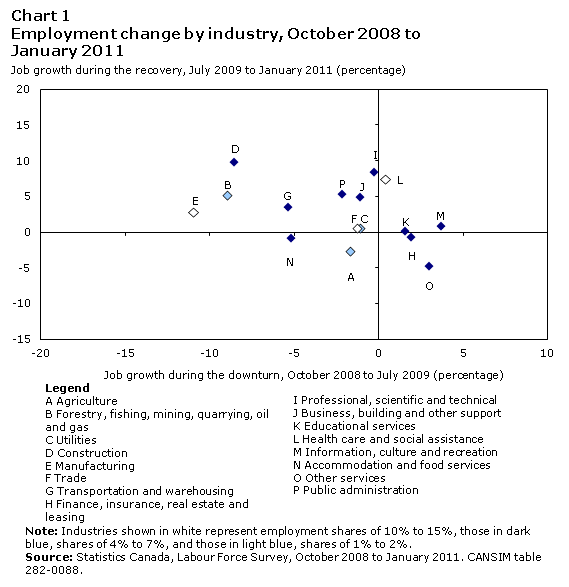
Using this classification, more than half of the industries (located in the upper left quadrant of Chart 1) were pro-cyclical, as they recouped jobs lost during the downturn. However, there was a lot of cross-industry variation among pro-cyclical industries.
Pro-cyclical industries can be further divided into three categories:
- those that did not recover as much employment as they lost (losses at least two times the level of gains)
- industries that eventually expanded after the downturn (gains at least two times the level of losses)
- industries that experienced a significant degree of recovery or did not experience large employment fluctuations (less than 2% growth or decline).
During the recent downturn and recovery period, the only industry that clearly did not recover from its losses was manufacturing, which employed one-tenth of the entire workforce. During the downturn, manufacturing industries declined significantly (-11%) and recovered only slightly during the recovery (+3%).Note 7
Pro-cyclical industries that expanded faster during the recovery included professional, scientific and technical services; business, building and other support services; and public administration (which collectively employed more than 15% of the workforce). Employment in professional, scientific and technical services fell by less than 1% during the downturn but grew by more than 8% during the recovery period. Public administration contracted by 2% and was followed by a 5% growth.
The industries that regained comparable employment numbers after the downturn or experienced some degree of recovery included construction (a 9% loss followed by 10% gain); transportation and warehousing (a 5% loss followed by a 3% gain); and natural resources. Other industries, like utilities and trade, did not experience major employment fluctuations over the period.Note 8
Industries in the upper right quadrant are those that expanded during both the downturn and the recovery. This applied to three industries—educational services; health care and social assistance; and information, culture and recreation. Health care and social assistance, in particular, grew modestly during the downturn but by 7% during the recovery period—a trend consistent with the aging of the population and the rising demand for health services.Note 9 In October 2008, nearly one-quarter of all workers were in industries that would eventually expand during both the downturn and the recovery.
Countercyclical industries are those that gained employment during the downturn and lost some during the recovery (lower right quadrant). In fact, two industries representing about 10% of the total workforce—finance, insurance, real estate and leasing and ’other’ services (such as repair and maintenance, personal, religious) were countercyclical. Other services—which have high rates of self-employment—saw a 3% job gain during the downturn but lost nearly 5% as the labour market picked up steam. Such results are not necessarily a surprise because self-employment generally increases during recessions.Note 10 Real estate—another sector with many self-employed workers—also picked up substantially during the recent downturn, hence explaining the growth in finance and real estate industries.
Finally, industries that were in the lower left quadrant declined during both the downturn and the recovery. In the late 2000s, two industries were categorized this way: agriculture, and accommodation and food services.Note 11 About 8% of the workforce was employed in these industries at the onset of the downturn.
More workers employed in industries that did not fully recover in the 1990s
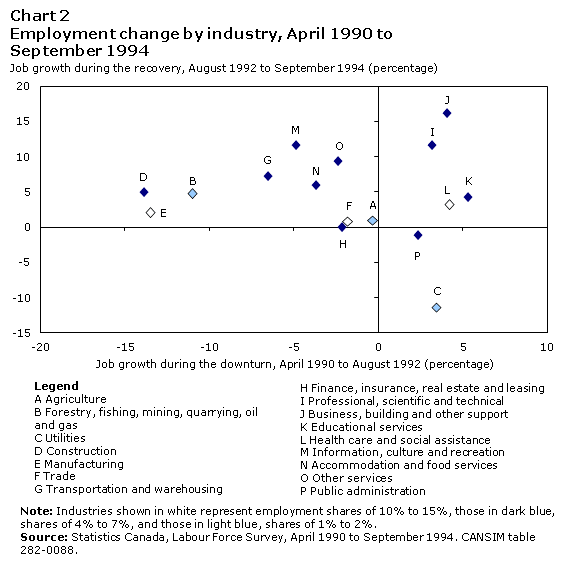
How do these results compare with the previous two downturns? In the early 1990s, three industries experienced large declines in employment in the early 1990s: manufacturing (-14%), construction (-14%) and natural resources (-11%), but employment did not fully recover in these industries (Chart 2). The 1990s, however, were characterized by significant employment growth in business, building, and other support services; and professional, scientific and technical services. Both sectors posted double-digit increases of 16% and 12%, respectively, during the recovery period.
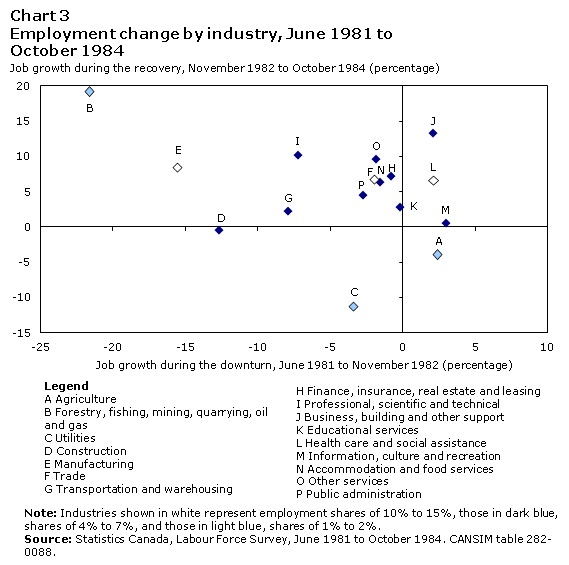
In the early 1980s, natural resources, manufacturing and construction also recorded the largest declines: 22%, 16%, and 13%, respectively (Chart 3). Contrary to the 1990s and 2000s, however, both natural resources and manufacturing industries recouped a large number of job losses during the recovery. Construction and utilities declined during both the downturn and the recovery—utilities, in particular, registered losses during the downturn (-3%) that extended well into the recovery (-11%). As was the case in the 1990s, business, building, and other support services experienced sustained growth, but to a lesser degree. However, professional, scientific and technical services had more of a cyclical pattern, losing 7% during the downturn but quickly expanding during the recovery (+10%).
During all three downturns, more workers were employed in industries that would eventually show pro-cyclical behaviour (Table 2). At the onset of the 1990s downturn, however, a larger percentage of employed people (about 25%) were in industries that did not recoup their losses, and another 7% were in constantly declining industries. In addition, many (23%) were employed in constantly growing industries, thereby suggesting that a large percentage of the Canadian workforce was exposed to significant changes during that period.
In comparison, in October 2008, more workers (47%) were employed in pro-cyclical industries that either made gains during the recovery, significantly recovered, or did not experience large fluctuations over the period. A large portion of the workforce was also employed in industries that gained employment both during the downturn and recovery (23%). In the 1980s, many people were employed in pro-cyclical industries that remained stable or expanded (more than 50%), but fewer were employed in industries that made gains during both the downturn and recovery (14%).
Table 2
More workers were employed in industries that did not recover in the early 1990s
| Beginning of the downturn | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| June 1981 | April 1990 | October 2008 | |
| percentage | |||
| Distribution of employment when the downturn began | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Declining during the downturn, growing during the recovery (pro-cyclical) | 74.8 | 63.2 | 58.5 |
| Gains more than 2 times the level of losses | 37.5 | 8.6 | 16.4 |
| Recovery, near-recovery or stable employment variation | 13.2 | 30.0 | 30.7 |
| Losses more than 2 times the level of gains | 24.2 | 24.5 | 11.4 |
| Growing during both the downturn and the recovery | 13.9 | 22.8 | 22.5 |
| Growing during the downturn, declining during the recovery (countercyclical) | 3.8 | 7.5 | 10.7 |
| Declining during both the downturn and the recovery | 7.4 | 6.5 | 8.3 |
|
Note: Industries that experienced less than 2% employment gains or losses over the period automatically qualified as 'stable.' Source: Statistics Canada, Labour Force Survey, 1981 to 1984, 1990 to 1994, 2008 to 2011. CANSIM table 282-0088. |
|||
Such results are not necessarily a surprise, given that the Canadian economy took a lot more time to recover in the early 1990s than during the last recession, and that employment growth did not immediately follow output growth.Note 12 The protracted employment growth, the long recovery and the higher degree of industrial change all suggest that labour market changes in the 1990s were more fundamental.Note 13, Note 14
What happened during the recent post-recovery period?
After reaching pre-downturn levels, employment continued increasing. Between January 2011 and February 2013, employment increased by 463,000 or 2.7% (Table 3).
Of the 463,000 increase in employment during the post-recovery period, 112,000 jobs were in accommodation and food services, followed by health care and social assistance (93,000)Note 15. Educational services (65,000) and construction (64,000) also grew significantly over the period. Together these four industries accounted for nearly three-quarters of all employment gains in the 25 months that followed the recovery. The relatively strong growth in health care and social assistance and in educational services suggests that non-business industries played a prominent role in employment growth in the aftermath of the downturn.
Table 3
Accommodation and food services, health care and social assistance, and educational services have accounted for a large portion of the increase since the recovery
| January 2011 | February 2013 | Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| thousand | thousand | percentage | ||
| Total employed, all industries | 17,233.5 | 17,696.4 | 462.9 | 2.7 |
| Agriculture | 308.7 | 319.6 | 10.9 | 3.5 |
| Forestry, fishing, mining, quarrying, oil and gas | 333.3 | 351.1 | 17.8 | 5.3 |
| Utilities | 145.4 | 133.6 | -11.8 | -8.1 |
| Construction | 1,245.9 | 1,309.4 | 63.5 | 5.1 |
| Manufacturing | 1,791.8 | 1,740.0 | -51.8 | -2.9 |
| Trade | 2,663.0 | 2,703.1 | 40.1 | 1.5 |
| Transportation and warehousing | 833.7 | 861.4 | 27.7 | 3.3 |
| Finance, insurance, real estate and leasing | 1,083.3 | 1,108.0 | 24.7 | 2.3 |
| Professional, scientific and technical | 1,290.0 | 1,326.7 | 36.7 | 2.8 |
| Business, building and other support | 698.3 | 706.0 | 7.7 | 1.1 |
| Educational services | 1,215.9 | 1,280.8 | 64.9 | 5.3 |
| Health care and social assistance | 2,072.5 | 2,165.6 | 93.1 | 4.5 |
| Information, culture and recreation | 779.8 | 785.6 | 5.8 | 0.7 |
| Accommodation and food | 1,031.1 | 1,143.3 | 112.2 | 10.9 |
| Other services | 753.5 | 777.2 | 23.7 | 3.1 |
| Public administration | 987.4 | 985.0 | -2.4 | -0.2 |
| Source: Statistics Canada, Labour Force Survey, 2011 and 2013. CANSIM table 282-0088. | ||||
Conversely, three industries recorded negative growth rates over the period—manufacturing contracted the most (-52,000), followed by utilities (-12,000) and public administration (-2,000). Changes were also unevenly distributed across occupations (see Occupational changes).
Table 4
Distribution of employment across industries at the onset of the downturn (October 2008) and more than two years after the recovery (February 2013)
| October 2008 | February 2013 | |
|---|---|---|
| percentage | ||
| Total employed, all industries | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Agriculture | 1.9 | 1.8 |
| Forestry, fishing, mining, quarrying, oil and gas | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Utilities | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Construction | 7.2 | 7.4 |
| Manufacturing | 11.4 | 9.8 |
| Trade | 15.6 | 15.3 |
| Transportation and warehousing | 5.0 | 4.9 |
| Finance, insurance, real estate and leasing | 6.2 | 6.3 |
| Professional, scientific and technical | 6.9 | 7.5 |
| Business, building and other support | 3.9 | 4.0 |
| Educational services | 7.0 | 7.2 |
| Health care and social assistance | 11.2 | 12.2 |
| Information, culture and recreation | 4.3 | 4.4 |
| Accommodation and food | 6.4 | 6.5 |
| Other services | 4.5 | 4.4 |
| Public administration | 5.6 | 5.6 |
| Source: Statistics Canada, Labour Force Survey, 2008 and 2013. CANSIM table 282-0088. | ||
Employment changes that took place during the downturn, the recovery and the two years that followed the recovery had an impact on the distribution of jobs across industries (Table 4). The proportion of employed individuals in manufacturing, for instance, declined from 11.4% to 9.8%, effectively extending a long-term decline that began in the early 2000s.Note 16 The proportion employed in health care and social assistance rose by a similar margin, from 11.2% to 12.2%, as did the shares of those employed in professional, scientific and technical services (from 6.9% to 7.5%). These two industries also expanded during the years that preceded the recent downturn.
Conclusion
The labour market is perpetually in a state of flux, with many jobs shifting away from some industries to others—a process that typically accelerates during recessions.Note 17 As in past recessions, not all industries followed a cyclical pattern of employment loss and creation during the latest employment downturn and recovery. In October 2008, more than 20% of workers were employed in industries that would eventually grow on a constant basis (especially health care); another 20% were in industries that either declined all the time or could not recoup their losses (like manufacturing), while nearly 50% were in industries that either fluctuated little over the period or created significantly more employment than they lost (such as professional, scientific and technical industries). During the 1990s, many more workers (31%) had been employed in industries that either declined all the time or did not fully recover after the downturn.
In the two years corresponding to the most recent post-recovery period, job growth was concentrated in four industries: accommodation and food services; health care and social assistance; educational services; and construction. Occupational data also indicated a relative concentration of growth in specific occupations, such as natural and applied sciences occupations; and trades, transport, equipment operators and related occupations (see Occupational changes). These newly created occupations require a fair degree of skill, with most of the newly created jobs requiring at least some college education training—particularly in trades and in engineering.
However, a good deal of reallocation also typically happens within industries (across firms of the same industry) to a greater extent than across industries. With the development of new administrative data sources, it will be interesting to see whether intra-industry labour reallocation was also a key feature of the recent downturn and subsequent recovery.
Sharanjit Uppal is a senior analyst in the Labour Statistics Division and
Sébastien LaRochelle-Côté is Chief Advisor in the Labour Statistics Division at Statistics Canada.
Notes
- See Cross 2011.
- See LaRochelle-Côté and Gilmore 2009.
- See Groshen and Potter 2003.
- Groshen and Potter (2003) examine layoff trends and job gains across industries during the 2001–2003 recession in the United States.
- A method largely inspired by Groshen and Potter (2003) was used to classify 2-digit NAICS industries based on employment variations during the downturn and the subsequent recovery. Employment changes at the 3-digit level could not be examined in the absence of seasonally adjusted data at that level. However, employment reallocation across firms within industries (i.e., intra-industry labour reallocation) is much larger than employment reallocation across industries (see Davis and Haltiwanger 1992). For a recent example using Canadian data, see Morissette et al. 2013.
- This is based on seasonally adjusted Labour Force Survey data by industry (see Statistics Canada 2013).
- The declines and increases in employment levels are calculated using the employment level at the start of the respective periods as the base. Hence, for example, a 1% increase in employment during the recovery does not fully offset a 1% decline in employment during the downturn.
- Interestingly, employment levels varied little across trade industries, which employed about 15% of the total Canadian workforce and remains one of the largest industrial groups.
- Health expenditures typically increase with age. A recent cost-driver analysis from the Canadian Institute for Health Information (2011) estimated that total per capita health expenditures were rising exponentially after age 65, from about $5,000 (in 2008) per person age 65 to 69 to $18,000 per person age 85 to 89. Furthermore, between 1998 and 2008, health care expenditures rose by 7.4% on average on a constant basis, with increases especially concentrated among older individuals.
- See LaRochelle-Côté 2010.
- Data were verified using the Survey of Employment, Payroll and Hours (SEPH), although the SEPH and LFS differ markedly in terms of reference period, data collection period, and population studied. For instance, the SEPH does not include self-employed workers. However, trends in labour market reallocation were mostly the same in industries that had a low proportion of self-employed individuals. Comparisons with industries that have higher portions of self-employed workers could not be made because self-employment is generally countercyclical, as shown in LaRochelle-Côté 2010.
- See Aaronson et al. 2004.
- The extent of industrial reallocation can also be quantified by the Lilien sectoral shift measure (see Lilien 1982; Leung and Cao 2009). A calculation using the Lilien measure from the month that marked the beginning of the employment downturn to the month that marked the return to the pre-downturn level produced the following results: 0.072 in 1981–1984, 0.081 in 1990–1994, and 0.050 in 2008–2011, confirming the higher degree of industrial reallocation in the early 1990s.
- The sources of structural changes in the labour market during the mid-1990s generated a good deal of commentary. At the time, the Canadian economy faced growing competition induced by trade agreements (see, for instance, Trefler 2004) and rising human capital growth that could have been fostered by labour market specialization and technological change (see Heisz et al. 2002). The labour market was also affected by high interest rates and sluggish product demand.
- Recall that employment declined both during the downturn and the recovery in food and accommodation services.
- See Bernard 2009. Between 1976 and 2012, the proportion of the workforce employed in manufacturing declined, even during periods of economic growth, from 19% in 1976 to 10% in 2012. On the other hand, some industries experienced continuous increases—professional, scientific and technical services, which employed less than 3% of the workforce in 1976 and more than 7% in 2012; and health care and social services, whose share increased from 8% in 1976 to nearly 12% in 2012.
- See Figura 2002.
Additional information
Related Articles
Data sources
Bibliographic references
- Date modified:
