Analysis in Brief
Analysis on supply chains in Canada, second quarter of 2022
Skip to text
Text begins
Challenges that have arisen since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic have shone a spotlight on the strength and resilience of supply chains. Many provinces and territories are feeling the effects from prior tightening and closing of borders, restrictions on the movement of people and goods, and the closure of businesses, which all had the potential to disrupt supply chains. As a result, the status of supply chains and the impact they have on their respective economies is of great interest.
Widespread global supply constraints in combination with pent-up consumer demand resulted in inflationary pressures. In fact, in April, Canadian consumer prices rose 6.8% year over year,Note a slight increase from March (+6.7%), the largest increase since January 1991 (+6.9%).Note In addition, the Industrial Product Price Index rose 0.8% month over month in April 2022 and 16.4% year over year,Note following the largest monthly and year over year gain since 1974 in March.Note Also, prices of raw materials purchased by manufacturers operating in Canada, as measured by the Raw Materials Price Index, decreased 2.0% on a monthly basis in April 2022 and rose 38.4% year over year.Note
From the beginning of April to early May 2022, Statistics Canada conducted the Canadian Survey on Business Conditions to better understand the current environment that businesses in Canada are operating in and their expectations moving forward. Based on the results of the survey, businesses expect supply chain issues to continue into the short term, specifically when acquiring inputs, products or supplies domestically and abroad, and maintaining inventory levels. Additionally, of those businesses that expected supply chain challenges, the vast majority expect the situation to stay the same or worsen over the next three months, and businesses plan to use various strategies to address supply chain issues. This article provides insights on the topic of supply chain challenges and the impacts of these issues on businesses in Canada.
Supply chain challenges anticipated to continue
Over one-quarter (28.2%) of businesses expect difficulty acquiring inputs, products or supplies domestically over the next three months.Note This proportion has decreased from the previous quarter, when nearly one-third (32.1%) of businesses anticipated challenges in this regard. Over half of businesses in agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting (52.9%) and manufacturing (52.0%) expect difficulty acquiring inputs, products or supplies domestically over the next three months. Of the businesses expecting difficulty acquiring inputs, products or supplies domestically, nearly three-fifths (57.3%) expect these challenges to continue for six months or more, up from the previous quarter (52.4%). Meanwhile, nearly one-third (30.8%) of businesses are uncertain how long these challenges will persist. Businesses in wholesale trade (68.8%) and professional, scientific and technical services (67.5%) were the most likely to expect this difficulty to continue being an obstacle for six months or more (Table 1).
Almost one-fifth (18.2%) of businesses expect difficulty acquiring inputs, products or supplies from abroad over the next three months. This is relatively unchanged from 18.1% of businesses in the previous quarter. About two-fifths of businesses in manufacturing (41.8%) and wholesale trade (37.9%) expect to experience this challenge over the next three months. Of businesses expecting difficulty acquiring inputs, products or supplies from abroad, almost three-fifths (58.2%) expect these challenges to continue for six months or more, down slightly from the previous quarter (62.5%). At the same time, almost one-third (31.2%) of businesses are uncertain how long these challenges will persist. Businesses in real estate and rental and leasing (70.9%) and arts, entertainment and recreation (70.0%) were the most likely to expect this difficulty to continue being an obstacle for six months or more (Table 1).
Nearly one-fifth (17.4%) of businesses expect maintaining inventory levels to be an obstacle over the next three months. This number has decreased slightly from the previous quarter, when one-fifth (20.8%) of businesses expected maintaining inventory levels to be an obstacle. Almost two-fifths (39.1%) of businesses in retail trade and nearly one-third of businesses in manufacturing (30.7%) and wholesale trade (30.2%) expect maintaining inventory levels to be a challenge over the next three months. Among businesses that expected maintaining inventory levels to be a challenge, over half (55.9%) expect these difficulties to continue for six months or more, up from the previous quarter (50.0%). However, nearly one-quarter (24.6%) of businesses are uncertain how long these challenges will persist. Businesses in agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting (63.7%); wholesale trade (63.6%); and manufacturing (63.5%) were the most likely to expect this obstacle to continue for six months or more (Table 1).
| Business expects difficulty acquiring inputs, products or supplies from within Canada for six months or more | Business expects difficulty acquiring inputs, products or supplies from abroad for six months or more | Business expects maintaining inventory levels to be an obstacle for six months or more | |
|---|---|---|---|
| All industries | 57.3 | 58.2 | 55.9 |
| Wholesale trade | 68.8 | 66.2 | 63.6 |
| Professional, scientific and technical services | 67.5 | 62.8 | 50.7 |
| Real estate and rental and leasing | 63.6 | 70.9 | 54.8 |
| Arts, entertainment and recreation | 62.3 | 70.0 | 60.8 |
| Retail trade | 61.3 | 59.0 | 63.0 |
| Agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting | 61.1 | 63.1 | 63.7 |
| Construction | 59.0 | 60.6 | 43.5 |
| Information and cultural industries | 59.0 | 46.8 | 28.8 |
| Manufacturing | 56.6 | 57.4 | 63.5 |
| Mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction | 56.5 | 47.4 | 46.6 |
| Accommodation and food services | 54.1 | 57.7 | 51.3 |
| Other services (except public administration) | 49.0 | 48.5 | 58.9 |
| Health care and social assistance | 45.8 | 45.2 | 42.9 |
| Transportation and warehousing | 40.3 | 44.7 | 37.2 |
|
Note: Respondents were asked from April 1 to May 6, 2022 their expectations on various obstacles over the next three months. Therefore, the three month period could range from April 1 to August 6, 2022 depending on when the business responded. If they reported that they expected difficulty acquiring inputs or supplies from within Canada or abroad, or maintaining inventory levels as obstacles, they were asked how long they expected these to continue being an obstacle. Source: Canadian Survey on Business Conditions, second quarter of 2022 (Table 33-10-0507-01). |
|||
Challenges worsening for businesses experiencing supply chain issues
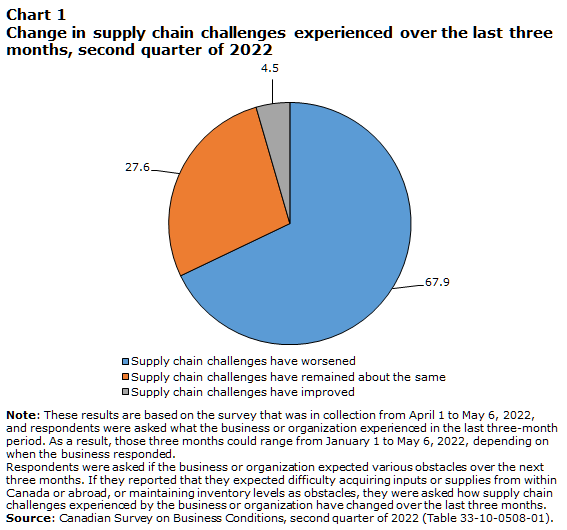
Of businesses that expected supply chain challenges (difficulty maintaining inventory levels, or acquiring inputs, products or supplies domestically or abroad) over the next three months, over two-thirds (67.9%) reported that challenges experienced by the business have worsened over the last three months. This figure has decreased from the previous quarter (71.9%). Leading factors that contributed to worsened supply chain challenges were increased delays in deliveries (84.1%); increased prices (78.5%) of inputs, products or supplies; and supply shortages that resulted in fewer inputs, products or supplies being available (75.7%), similar to the previous quarter (84.7%, 76.3%, and 75.8% respectively). Over one-quarter (27.6%) of businesses that expected supply chain challenges reported that these challenges have remained about the same over the last three months, and 4.5% said that supply chain challenges have improved.
Data table for Chart 1
| Supply chain challenges have worsened | Supply chain challenges have remained about the same | Supply chain challenges have improved | |
|---|---|---|---|
| percent | |||
| Businesses that expect supply chain challenges | 67.9 | 27.6 | 4.5 |
|
Note: These results are based on the survey that was in collection from April 1 to May 6, 2022, and respondents were asked what the business or organization experienced in the last three-month period. As a result, those three months could range from January 1 to May 6, 2022, depending on when the business responded. Respondents were asked if the business or organization expected various obstacles over the next three months. If they reported that they expected difficulty acquiring inputs or supplies from within Canada or abroad, or maintaining inventory levels as obstacles, they were asked how supply chain challenges experienced by the business or organization have changed over the last three months. Source: Canadian Survey on Business Conditions, second quarter of 2022 (Table 33-10-0508-01). |
|||
Among businesses that expect supply chain challenges over the next three months, businesses in professional, scientific and technical services (85.6%); accommodation and food services (72.5%); and manufacturing (70.7%) were the most likely industries to report that supply chain challenges have worsened. In contrast, two-fifths (40.6%) of businesses in arts, entertainment and recreation reported that supply chain challenges have remained about the same.
Similar to the previous quarter, the vast majority of businesses expect supply chain challenges to either worsen or remain about the same over the next three months. Specifically, over one-third (35.9%) of businesses expect supply chain challenges to worsen, while over half (56.0%) expect the situation to remain about the same. Businesses in agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting (48.7%) and accommodation and food services (48.6%) were the most likely industries to expect supply chain challenges to worsen over the next three months. At the same time, 8.1% of businesses expect supply chain challenges to improve over the next three months.
Planned adjustments to supply chains
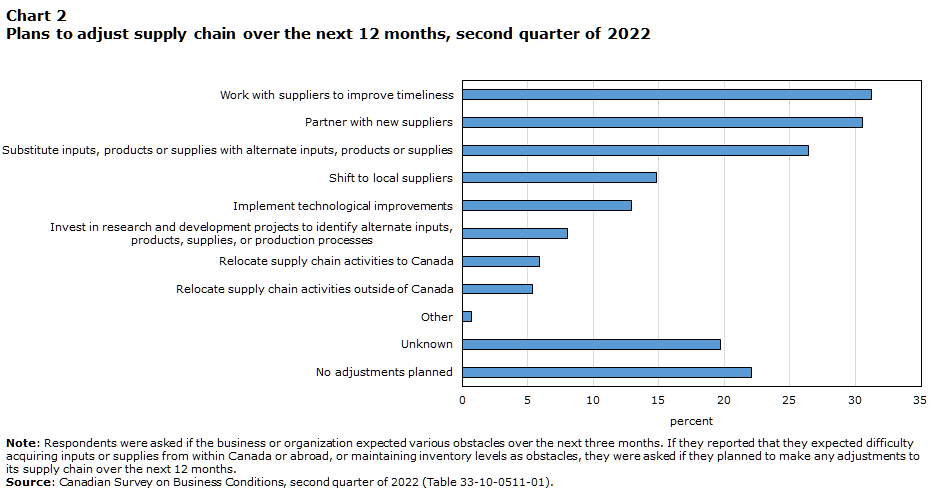
Businesses expect supply chain challenges over the next three months and have planned various adjustments to address them over the next 12 months. Nearly one-third of these businesses plan to work with suppliers to improve timeliness (31.2%) and partner with new suppliers (30.5%), and over one-quarter (26.4%) plan to substitute inputs, products or supplies with alternate inputs, products or supplies. Meanwhile, 14.8% businesses plan to shift to local suppliers, with businesses in arts, entertainment and recreation (32.4%) being most likely to do so. Nearly one-fifth (19.7%) of businesses were uncertain of plans to adjust their supply chain, and more than one-fifth (22.1%) had no plans to adjust their supply chain over the next 12 months.
Data table for Chart 2
| Adjustments planned for supply chain | Percent |
|---|---|
| Work with suppliers to improve timeliness | 31.2 |
| Partner with new suppliers | 30.5 |
| Substitute inputs, products or supplies with alternate inputs, products or supplies | 26.4 |
| Shift to local suppliers | 14.8 |
| Implement technological improvements | 12.9 |
| Invest in research and development projects to identify alternate inputs, products, supplies, or production processes | 8.0 |
| Relocate supply chain activities to Canada | 5.9 |
| Relocate supply chain activities outside of Canada | 5.4 |
| Other | 0.7 |
| Unknown | 19.7 |
| No adjustments planned | 22.1 |
|
Note: Respondents were asked if the business or organization expected various obstacles over the next three months. If they reported that they expected difficulty acquiring inputs or supplies from within Canada or abroad, or maintaining inventory levels as obstacles, they were asked if they planned to make any adjustments to its supply chain over the next 12 months. Source: Canadian Survey on Business Conditions, second quarter of 2022 (Table 33-10-0511-01). |
|
Vast majority of inputs, products or supplies sourced domestically
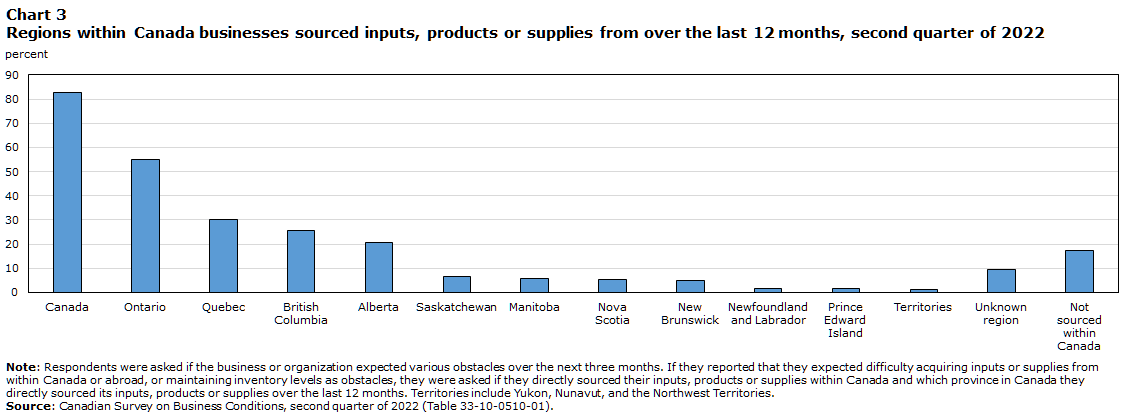
Of businesses that expect supply chain challenges over the next three months, most (82.6%) sourced inputs, products or supplies within Canada in the last 12 months. In particular, over half (55.2%) of these businesses sourced inputs, products or supplies from Ontario, almost one-third (30.3%) sourced from Quebec, one-quarter (25.8%) sourced from British Columbia, and one-fifth (20.6%) sourced from Alberta.
Data table for Chart 3
| Regions within Canada businesses sourced inputs, products or supplies from | Percent |
|---|---|
| Canada | 82.6 |
| Ontario | 55.2 |
| Quebec | 30.3 |
| British Columbia | 25.8 |
| Alberta | 20.6 |
| Saskatchewan | 6.8 |
| Manitoba | 5.7 |
| Nova Scotia | 5.5 |
| New Brunswick | 4.9 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 1.7 |
| Prince Edward Island | 1.6 |
| Territories | 1.3 |
| Unknown region | 9.4 |
| Not sourced within Canada | 17.4 |
|
Note: Respondents were asked if the business or organization expected various obstacles over the next three months. If they reported that they expected difficulty acquiring inputs or supplies from within Canada or abroad, or maintaining inventory levels as obstacles, they were asked if they directly sourced their inputs, products or supplies within Canada and which province in Canada they directly sourced its inputs, products or supplies over the last 12 months. Territories include Yukon, Nunavut, and the Northwest Territories. Source: Canadian Survey on Business Conditions, second quarter of 2022 (Table 33-10-0510-01). |
|
Businesses in mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction (91.8%); construction (90.4%); and agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting (89.9%) were the most likely to source their inputs, products or supplies within Canada in the last 12 months. Businesses in administrative and support, waste management and remediation services (34.3 %); transportation and warehousing (31.0 %); and real estate and rental and leasing (30.3%) were the least likely to have sourced any inputs, products or supplies within Canada in the last 12 months.
Methodology
From April 1 to May 6, 2022, representatives from businesses across Canada were invited to take part in an online questionnaire about business conditions and business expectations moving forward. The Canadian Survey on Business Conditions uses a stratified random sample of business establishments with employees classified by geography, industry sector, and size. An estimation of proportions is done using calibrated weights to calculate the population totals in the domains of interest. The total sample size for this iteration of the survey is 35,775 and results are based on responses from a total of 16,678 businesses or organizations.
References
Statistics Canada. 2022. Canadian Survey on Business Conditions, second quarter of 2022.
- Date modified: