Canada's international investment position, second quarter 2020
Archived Content
Information identified as archived is provided for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It is not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards and has not been altered or updated since it was archived. Please "contact us" to request a format other than those available.
Released: 2020-09-10
$1,102.2 billion
Second quarter 2020
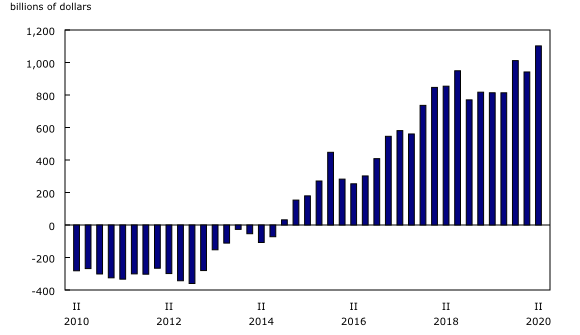
Canada's net foreign asset position increased by $160.5 billion to $1,102.2 billion at the end of the second quarter. This increase was largely attributable to the recovery of global stock markets, which had experienced considerable losses at the end of the first quarter.
Despite ongoing current account deficits and the need for foreign borrowing, Canada's net foreign asset position continued its upward trend in the second quarter to reach unprecedented levels.
Recent quarterly fluctuations in the net international investment position are strongly linked to the performance of global equity markets. Changing stock market conditions, driven by shocks such as the COVID-19 pandemic, tend to affect Canada's international assets more severely than its liabilities, as a higher proportion of assets (68.0%) than liabilities (39.0%) are held in the form of equities.
The major stock markets recorded significant gains in the second quarter. Over the quarter, the Canadian stock market increased by 16.0%, the US stock market grew by 20.0% and the European stock market rose by 16.0%.
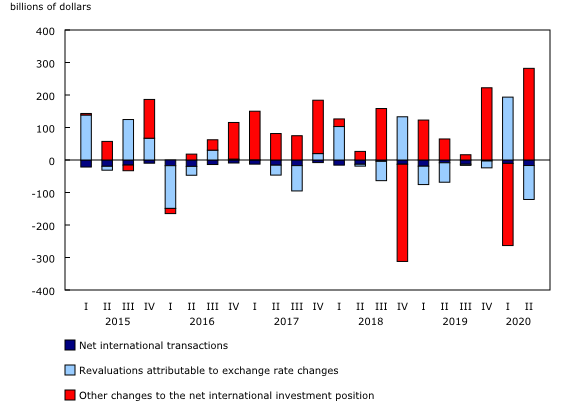
The revaluation effect from fluctuations in exchange rates (-$104.4 billion) lowered the value of assets more than that of liabilities, moderating the overall increase in Canada's net foreign asset position. Over the quarter, the Canadian dollar gained 4.1% against the US dollar, 1.8% against the euro, 4.6% against the UK pound sterling and 4.0% against the Japanese yen. At the end of the second quarter, 96.5% of Canada's international assets were denominated in foreign currencies, compared with 41.3% of its international liabilities.
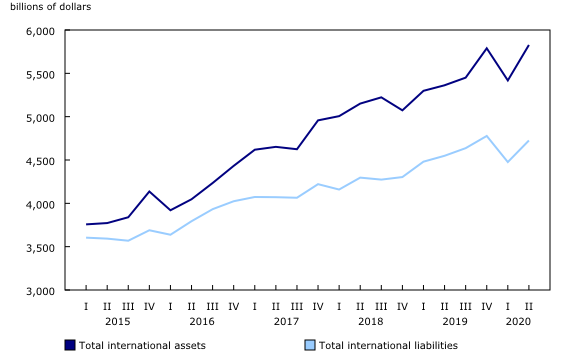
Canada's international assets and liabilities increase on higher equity prices
Canada's international assets were up by $409.5 billion to $5,827.5 billion in the second quarter, exceeding the levels recorded at the end of 2019. The upward revaluation from higher foreign equity prices and, to a lesser extent, large acquisitions of foreign shares contributed to the increase. The revaluation effect (-$166.7 billion) attributable to the Canadian dollar appreciating against all major foreign currencies attenuated the growth.
On the other side of the ledger, Canada's international liabilities were up by $249.0 billion to $4,725.3 billion, led by higher equity prices and record foreign investment in Canadian debt securities. However, the growth was moderated by the downward revaluation effect (-$62.3 billion) from the appreciation of the Canadian dollar.
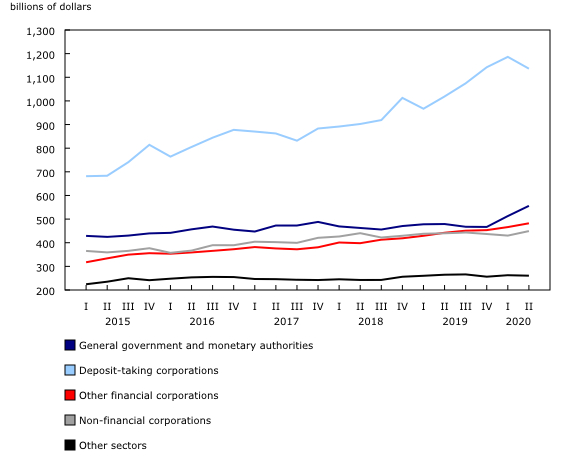
Government sector's gross external debt reaches a record high
Canada's gross external debt, or the value of Canadian debt instruments held by foreign investors, was up by $26.1 billion to $2,884.4 billion in the second quarter, led by the government sector.
The government sector's gross external debt grew by $42.9 billion, to reach an unprecedented level of $555.2 billion. Foreign borrowing in the form of debt securities accounted for the bulk of the increase. To support enterprises and households impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, the federal government substantially expanded its overall borrowing activity in the quarter, resulting in a record amount of this debt being acquired by foreign investors.
The financial sector, mainly deposit-taking corporations, saw its gross external debt decrease by $34.0 billion to $1,618.5 billion. The increase from new bonds placed in foreign markets was more than offset by a reduction in deposit liabilities with non-residents. Meanwhile, gross external debt of non-financial corporations rose by $19.1 billion to $449.3 billion, mostly because of increased non-resident bond holdings.
Note to readers
Currency valuation
The value of assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies is converted to Canadian dollars at the end of each period for which a balance sheet is calculated. When the Canadian dollar is appreciating in value, the restatement of the value of these assets and liabilities in Canadian dollars lowers the recorded value. The opposite is true when the Canadian dollar is depreciating.
Definitions
The international investment position is the value and composition of Canada's assets and liabilities to the rest of the world.
Canada's net international investment position is the difference between Canada's assets and liabilities to the rest of the world. An excess of international liabilities over international assets can be referred to as Canada's net foreign debt. An excess of international assets over international liabilities can be referred to as Canada's net foreign assets.
Foreign direct investment is presented on an asset–liability principle basis (that is, a gross basis) in the international investment position. Foreign direct investment can also be presented on a directional principle basis (that is, a net basis), as shown in supplementary foreign direct investment tables 36-10-0008-01 and 36-10-0009-01. The difference between the two foreign direct investment conceptual presentations resides in the classification of reverse investment such as (1) Canadian affiliates' claims on foreign parents and (2) Canadian parents' liabilities to foreign affiliates. Under the asset–liability presentation, (1) is classified as an asset and included in direct investment assets, and (2) is classified as a liability and included in direct investment liabilities.
Products
The Economic accounts statistics portal, accessible from the Subjects module on our website, features an up-to-date portrait of national and provincial economies and their structures.
The Methodological Guide: Canadian System of Macroeconomic Accounts (13-607-X) is available.
The User Guide: Canadian System of Macroeconomic Accounts (13-606-G) is also available.
The Canada and the World Statistics Hub (13-609-X) is available online. This product illustrates the nature and extent of Canada's economic and financial relationship with the world through interactive graphs and tables. This product provides easy access to information on trade, investment, employment and travel between Canada and a number of countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Mexico, China and Japan.
Contact information
For more information, contact us (toll-free 1-800-263-1136; 514-283-8300; STATCAN.infostats-infostats.STATCAN@canada.ca).
To enquire about the concepts, methods or data quality of this release, contact Vicky Gélinas (613-716-2828; vicky.gelinas@canada.ca), International Accounts and Trade Division.
- Date modified: